Introduction
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and can cause complications for both the mother and the baby if left unmanaged. Early detection and management of gestational diabetes are crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. In this blog, we’ll explain how to spot and manage gestational diabetes early, particularly in the Indian context, and why regular monitoring of pregnancy sugar levels is essential.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin during pregnancy, leading to high blood sugar levels. This condition usually develops around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy and affects about 3-8% of pregnancies globally. Although it typically resolves after childbirth, it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both mother and child.
How to Spot Gestational Diabetes
Some women may experience gestational diabetes symptoms, while others may have no symptoms at all. Common signs to look out for include:
- Increased thirst and dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue and feeling sluggish
- Blurred vision
- Increased hunger, even after eating
However, many women with gestational diabetes have no noticeable symptoms, which is why routine screening is so important.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Certain women may be at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes:
- Age: Women over the age of 25 are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese before pregnancy increases the risk.
- Family history: Having a close family member with diabetes increases the risk.
- Previous gestational diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are at higher risk.
How to Manage Gestational Diabetes Early
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes can prevent complications. Here are steps to manage the condition:
1. Screening and Diagnosis
Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed through a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. If you have risk factors, your doctor may recommend earlier testing. If diagnosed, your healthcare provider will develop a management plan tailored to your needs.
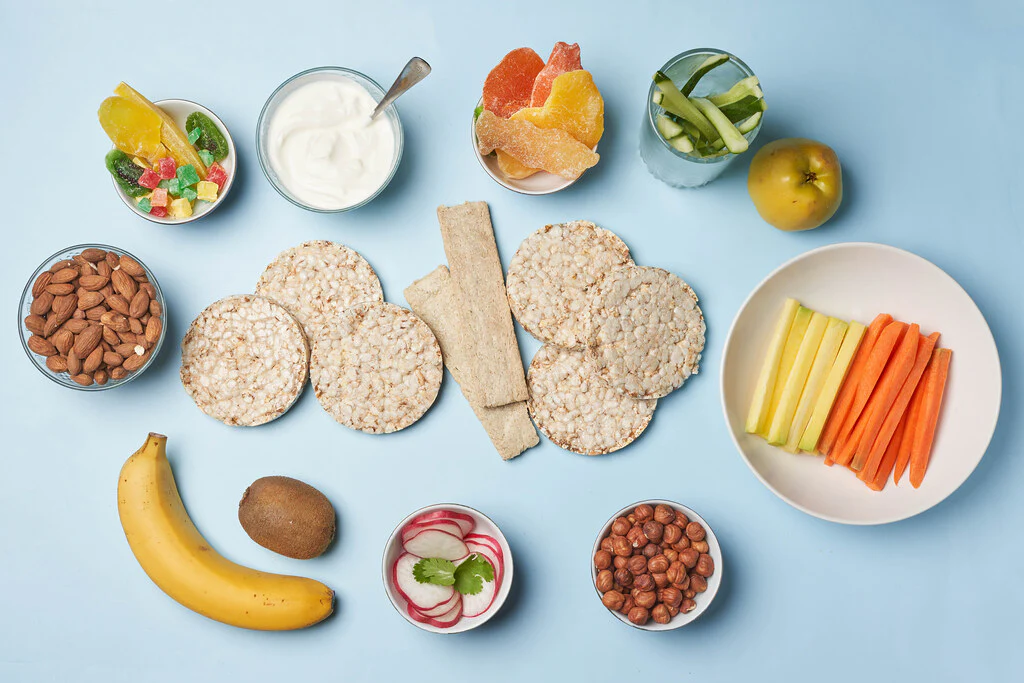
2. Healthy Diet
A balanced, diabetes-friendly diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Focus on:
- Whole grains instead of refined carbohydrates
- Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and legumes
- Non-starchy vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and cauliflower
- Limited sugary foods and processed snacks
Work with a nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that helps keep your blood sugar levels stable.
3. Regular Exercise
Moderate exercise, such as walking or pregnancy-safe yoga, can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week, but always consult your doctor before starting any exercise program during pregnancy.
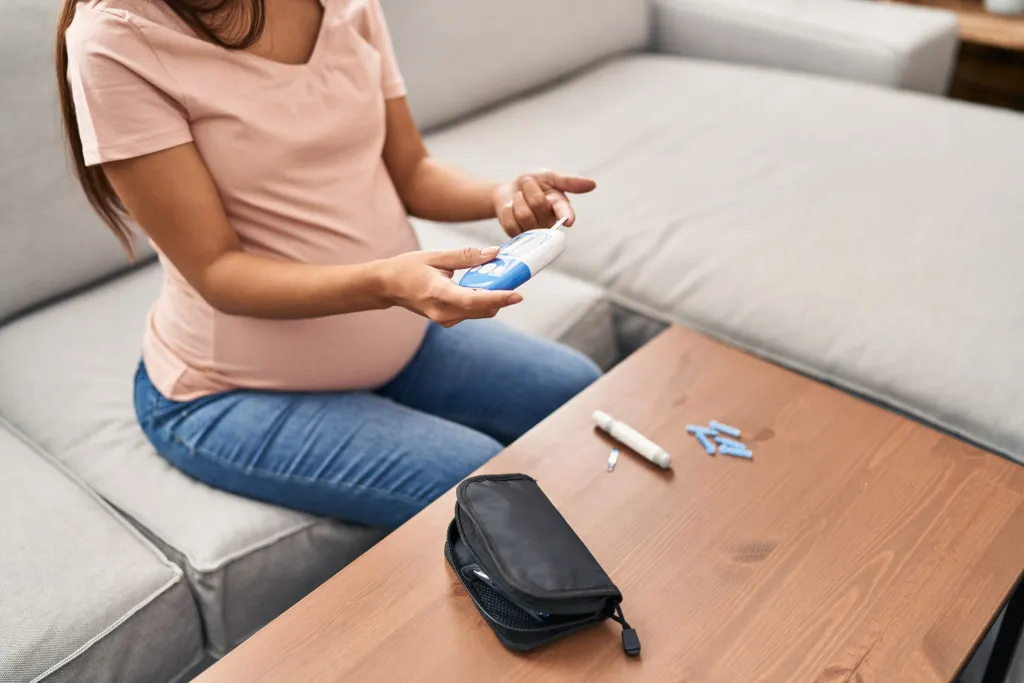
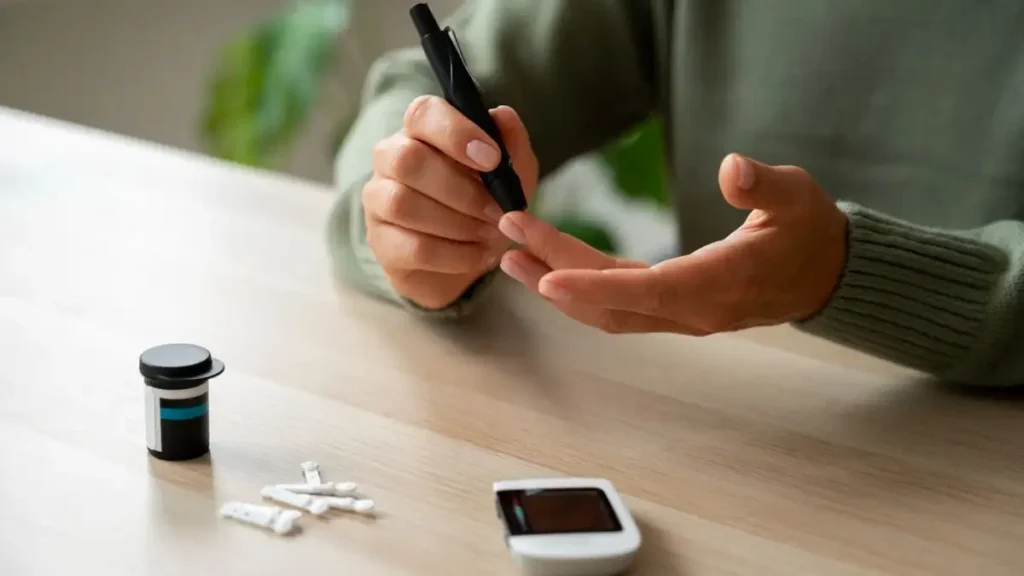
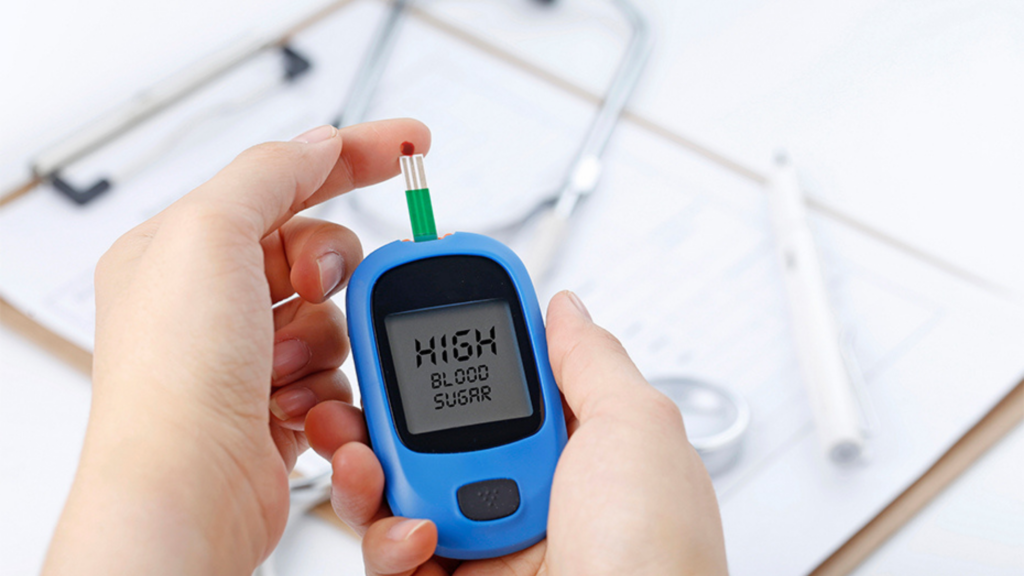
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of pregnancy sugar levels is critical in managing gestational diabetes. Your doctor may advise you to check your blood sugar several times a day to ensure that your levels remain within the target range. Keeping a log of your readings will help your healthcare team make necessary adjustments to your diet or medication.
5. Medication
In some cases, insulin or oral medications may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. Insulin does not cross the placenta, making it a safe option for controlling blood sugar during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes are essential for the health of both the mother and the baby. Regular screenings, a healthy diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring are key components of managing the condition. If you’re pregnant and at risk of gestational diabetes, schedule regular checkups with your healthcare provider, and remember that MV Diabetes Hospital is here to support you with comprehensive care and management for a healthy pregnancy.