Best Diet Plan for Type 2 Diabetes Patients in India
Diet plays the most critical role in managing Type 2 diabetes. The right Indian diet can control blood sugar, reduce medication dependency, and prevent complications.
Key Principles of a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
- Low glycaemic load
- High fiber content
- Balanced protein intake
- Healthy fats
- Controlled portion sizes
Foods to Include
Whole Grains
- Brown rice
- Millets (ragi, jowar)
- Whole wheat chapati
Vegetables
- Leafy greens
- Bitter gourd
- Bottle gourd
- Beans
Proteins
- Dal and legumes
- Eggs
- Fish
- Paneer (in moderation)
Foods to Avoid or Limit
- White rice
- Sugar and sweets
- Refined flour
- Sugary beverages
- Deep-fried foods
Sample Indian Diet Plan (Simplified)
Breakfast: Vegetable omelette + multigrain toast
Mid-morning: Fruit (low glycaemic)
Lunch: Brown rice + dal + vegetables
Evening: Nuts or buttermilk
Dinner: Chapati + vegetable curry + protein
Importance of Meal Timing
Eating at regular intervals helps avoid sugar spikes and crashes.
Common Diet Mistakes
- Skipping meals
- Overeating fruits
- Eliminating carbs completely
- Following online “crash diets”
Personalised Diet Matters
No single diet fits all. Age, weight, activity level, and sugar readings matter.
MV Diabetes offers customised diet planning tailored to Indian lifestyles.
Can Diabetes Be Reversed? Myths vs Facts
The question “Can diabetes be reversed?” is one of the most searched diabetes-related queries in India. The answer depends on the type of diabetes, the stage of diagnosis, and lifestyle changes.
Let’s separate myths from medical facts.
Understanding the Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: Autoimmune condition (not reversible)
- Type 2 Diabetes: Lifestyle-related and potentially reversible in early stages
- Prediabetes: Highly reversible with timely action
Myth 1: Diabetes Can Be Cured Completely
❌ Myth
There is currently no permanent cure for diabetes.
✅ Fact
Type 2 diabetes can be put into remission, meaning blood sugar levels remain normal without medication for long periods.
Myth 2: Only Medications Can Control Diabetes
❌ Myth
Medication alone is not enough.
✅ Fact
Diet, physical activity, weight management, and stress control play a major role in diabetes reversal.
Myth 3: Once You Start Medication, You Can Never Stop
❌ Myth
✅ Fact
With medical supervision, improved lifestyle habits can reduce or even eliminate medication dependency in early Type 2 diabetes.
Myth 4: Reversal Means You Can Eat Anything
❌ Myth
✅ Fact
Even in remission, healthy eating and regular monitoring are essential to prevent relapse.
How Diabetes Reversal Actually Works
1. Weight Reduction
Losing even 5–10% of body weight improves insulin sensitivity significantly.
2. Dietary Changes
A diabetes-friendly Indian diet includes:
- Whole grains
- High-fiber vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Controlled carbohydrate intake
3. Regular Physical Activity
- Walking 30–45 minutes daily
- Strength training improves insulin usage
4. Medical Supervision
Attempting reversal without medical guidance can be dangerous. Regular monitoring ensures safe progress.
Who Can Reverse Diabetes?
You may be a good candidate if:
- Diagnosed within the last 5–6 years
- HbA1c levels are moderately elevated
- Willing to make long-term lifestyle changes
The Role of MV Diabetes
MV Diabetes focuses on:
- Evidence-based treatment
- Lifestyle-oriented diabetes management
- Personalised diet and activity plans
- Continuous monitoring
The Truth About Reversal
Diabetes reversal is not a shortcut. It requires commitment, discipline, and expert guidance—but it is possible for many people.
Early Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Diabetes is no longer a condition that appears suddenly. In most cases, the body shows early warning signs long before blood sugar levels become dangerously high. Unfortunately, many people ignore these symptoms or mistake them for everyday fatigue or stress.
Understanding the early signs of diabetes can help you take timely action, prevent complications, and maintain long-term health.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either:
- Does not produce enough insulin, or
- Cannot effectively use insulin
This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can damage vital organs over time.
Early Signs of Diabetes You Should Watch For
1. Frequent Urination
One of the most common early symptoms of diabetes is urinating more often, especially at night. Excess sugar in the blood forces the kidneys to work harder to remove it, leading to frequent bathroom trips.
2. Excessive Thirst
Frequent urination causes dehydration, which leads to constant thirst. Drinking more water but still feeling thirsty can be an early red flag.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
If your body can’t use glucose properly, it starts burning fat and muscle for energy. This can cause sudden weight loss, even when your diet hasn’t changed.
4. Constant Fatigue
High blood sugar prevents glucose from entering cells, leaving your body without enough energy. Persistent tiredness despite adequate sleep may signal rising sugar levels.
5. Increased Hunger
Feeling hungry soon after eating can indicate insulin resistance. Your body isn’t able to use glucose efficiently, so it keeps signaling hunger.
6. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar can cause fluid shifts in the eyes, leading to temporary blurred vision. If untreated, this can progress to long-term eye damage.
7. Slow Healing of Wounds
Cuts, infections, or bruises that take longer to heal may indicate poor blood circulation caused by diabetes.
8. Tingling or Numbness
Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) often begins with tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
You may be at higher risk if you:
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are overweight or physically inactive
- Have high blood pressure or cholesterol
- Are over 35 years of age
- Had gestational diabetes
When Should You Get Tested?
If you notice two or more symptoms, it’s important to undergo:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test
- HbA1c Test
- Post-meal Blood Sugar Test
Early diagnosis can prevent complications affecting the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Why Early Detection Matters
Detecting diabetes early allows:
- Better sugar control
- Lifestyle-based reversal (in early stages)
- Reduced dependency on medications
- Prevention of long-term complications
Take Action Early
Ignoring early signs can lead to irreversible damage. A simple blood test and expert guidance can make a life-changing difference.
MV Diabetes focuses on early detection, personalised treatment plans, and long-term diabetic care tailored to Indian lifestyles.
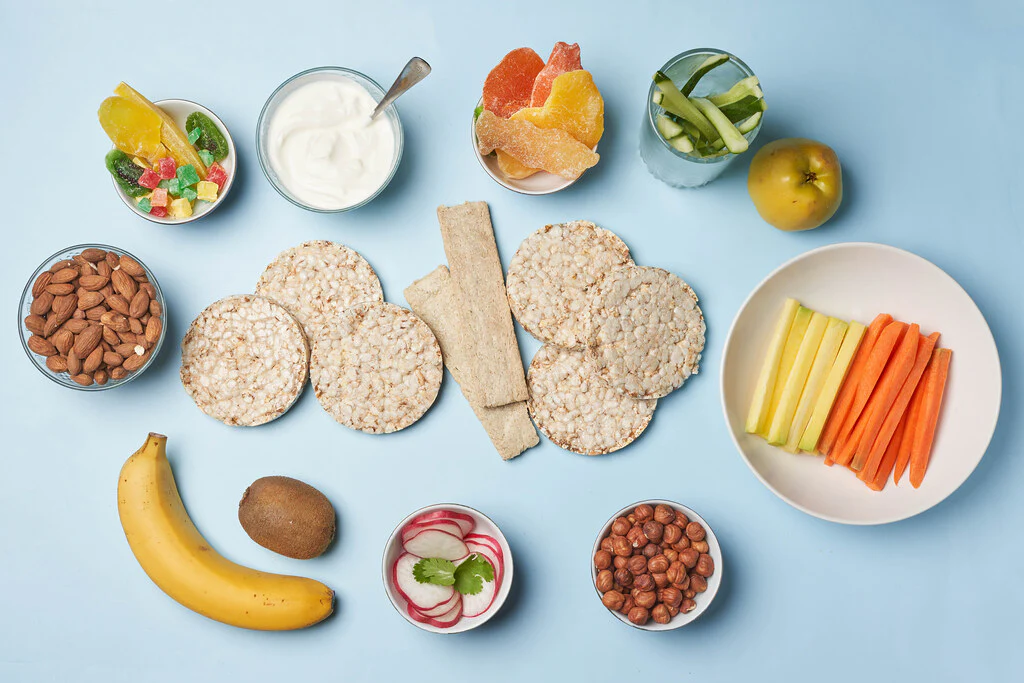

Diabetes-Friendly Snacks You Can Eat Guilt-Free
Introduction
Managing diabetes requires a healthy, balanced diet, and that includes choosing the right snacks. Many traditional snacks are high in sugar and carbs, which can cause blood sugar spikes. However, with the right choices, diabetic snacks can be both delicious and healthy. In this blog, we’ll guide you through diabetes-friendly snacks that will help manage your blood sugar while satisfying your cravings. Whether you’re in need of a mid-afternoon pick-me-up or a post-workout snack, these options are perfect for snacks for diabetics in India.
Why Snacking Matters for Diabetics
Snacking plays an important role in keeping blood sugar levels stable. If you have diabetes, it’s crucial to choose snacks that:
- Stabilize blood sugar: Avoid foods that cause quick spikes in blood sugar.
- Provide sustained energy: Opt for snacks that provide slow-releasing energy throughout the day.
- Include fiber and protein: These nutrients help regulate blood sugar levels and keep you full for longer.
Diabetes-Friendly Snack Ideas
1. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are packed with healthy fats, fiber, and protein. They help keep you full while stabilizing your blood sugar levels. Seeds like chia, flax, and sunflower seeds are also great options.
Benefits:
- Rich in monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids.
- High in fiber to aid digestion and control blood sugar levels.
Tip: Limit portion sizes to avoid excess calorie intake, as nuts are calorie-dense.
2. Greek Yogurt with Berries
Greek yogurt is rich in protein and low in carbohydrates, making it an ideal snack for people with diabetes. Pairing it with fresh berries adds a touch of sweetness while providing antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber.
Benefits:
- Protein-rich for sustained energy.
- Low in sugar compared to regular yogurt.
Tip: Choose plain, unsweetened Greek yogurt and add your own fresh berries or a drizzle of honey for natural sweetness.
3. Vegetable Sticks with Hummus
Crunchy vegetables like cucumber, carrots, and celery are low in calories and carbohydrates, making them perfect for a diabetes-friendly snack. Pair them with hummus for an extra boost of flavor and protein.
Benefits:
- Low-calorie, high-fiber veggies.
- Hummus provides protein and healthy fats to keep you satisfied.
Tip: Stick to fresh, raw vegetables to avoid added sugars or preservatives found in some packaged products.
4. Apple Slices with Peanut Butter
An apple paired with a tablespoon of natural peanut butter makes for a delicious and satisfying snack. Apples provide fiber and antioxidants, while peanut butter offers protein and healthy fats.
Benefits:
- High in fiber for better blood sugar control.
- Protein and fat from peanut butter help keep you full.
Tip: Choose unsweetened peanut butter to avoid added sugars.
5. Hard-Boiled Eggs
Hard-boiled eggs are a low-carb, high-protein snack that’s perfect for managing blood sugar levels. They’re also portable and easy to prepare in advance.
Benefits:
- Rich in protein and healthy fats.
- Low in carbs, making them ideal for diabetics.
Tip: Pair with a small serving of vegetables or nuts for a balanced snack.
Conclusion
When managing diabetes, choosing the right diabetic-friendly snacks is essential for controlling blood sugar levels and staying energized throughout the day. Incorporating options like nuts, Greek yogurt, vegetable sticks with hummus, and hard-boiled eggs will help you maintain a balanced diet without compromising on taste. For more diabetic diet tips and personalized nutrition plans, visit MV Diabetes Hospital for expert advice and guidance.
Diabetes and Skin Health: Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Introduction
Diabetes can affect more than just your blood sugar levels—it can also have a significant impact on your skin health. In fact, diabetic skin issues are common and can serve as warning signs of poor blood sugar control. It’s essential for individuals with diabetes to be vigilant about their skin health to prevent complications. At MV Diabetes Hospital, we guide our patients through understanding and managing skin symptoms of diabetes. In this blog, we’ll highlight the most common skin issues associated with diabetes and what to do about them.
Common Diabetic Skin Issues
1. Dry Skin
High blood sugar levels can cause the skin to lose moisture, leading to dry, flaky skin. This condition is particularly common on the legs, feet, and hands. Over time, untreated dry skin can crack and become more susceptible to infections.
Management Tips:
- Use moisturizing creams that are rich in emollients like glycerin and shea butter.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support skin moisture.
2. Infections
People with diabetes are more prone to skin infections due to poor circulation and a weakened immune system. Common infections include:
- Fungal infections: Such as athlete’s foot or yeast infections, especially in warm, moist areas.
- Bacterial infections: Like boils and abscesses.
Management Tips:
- Keep skin clean and dry, especially in skin folds.
- Use antifungal or antibacterial creams as prescribed by your doctor.
3. Diabetic Dermopathy
Diabetic dermopathy appears as small, round, dark spots on the skin, typically on the legs. These spots are harmless but can be a sign of long-term high blood sugar.
Management Tips:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels to prevent further damage.
- Moisturizing and gentle skin care can help with the appearance of the spots.
4. Acanthosis Nigricans
This condition is characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin, typically found on the neck, armpits, or groin. It is often a sign of insulin resistance and is common in people with type 2 diabetes.
Management Tips:
- Control blood sugar levels to prevent further progression.
- Regular visits to a dermatologist can help manage the appearance of these patches.
5. Blisters
Blisters can appear on the skin, especially on the feet, and are often caused by high blood sugar levels. These blisters are often painless and resemble burn blisters, but they require prompt treatment to avoid infection.
Management Tips:
- Keep feet dry and wear diabetic-friendly footwear.
- Seek medical advice if blisters develop to prevent infection.
How to Protect Your Skin
- Maintain good blood sugar control: Consistently managing your blood sugar is key to preventing most diabetic skin issues.
- Regular skin checks: Perform regular checks to identify any changes in your skin. Early intervention can prevent complications.
- Moisturize daily: Keep your skin hydrated with diabetic-friendly moisturizers to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and hydration will help maintain healthy skin and overall wellness.
Conclusion
Diabetes can lead to several skin issues, from dryness and infections to more serious conditions like diabetic dermopathy and acanthosis nigricans. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, maintaining proper skin hygiene, and moisturizing can help manage and prevent these issues. If you notice any changes in your skin, consult with a healthcare provider. MV Diabetes Hospital is here to help you manage diabetes and its associated complications, ensuring you maintain healthy skin for life.
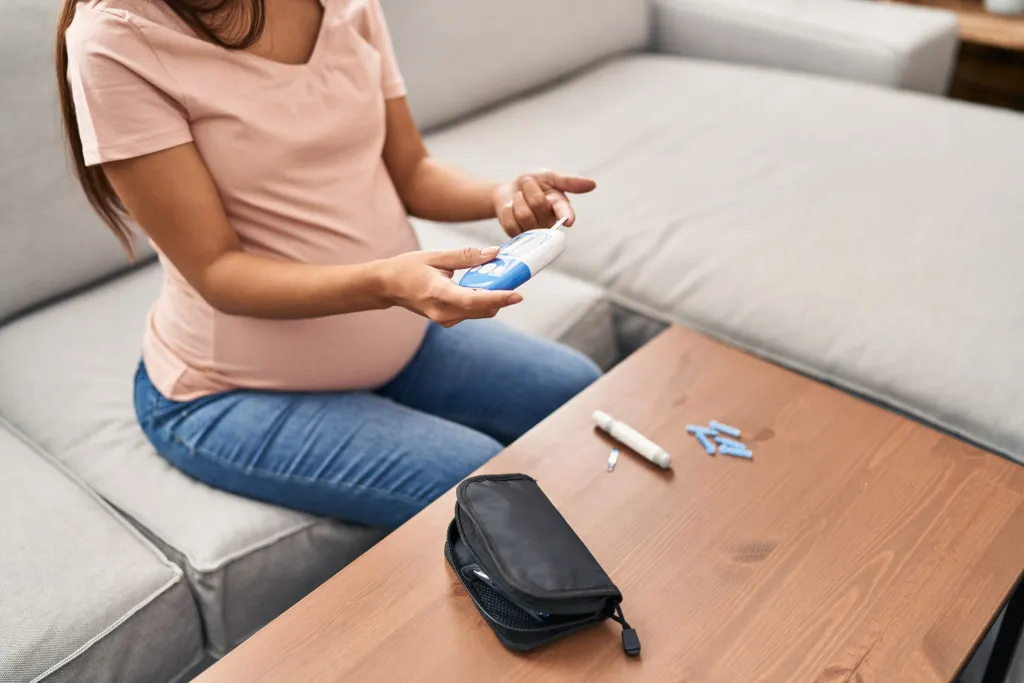

How to Spot and Manage Gestational Diabetes Early
Introduction
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and can cause complications for both the mother and the baby if left unmanaged. Early detection and management of gestational diabetes are crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. In this blog, we’ll explain how to spot and manage gestational diabetes early, particularly in the Indian context, and why regular monitoring of pregnancy sugar levels is essential.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin during pregnancy, leading to high blood sugar levels. This condition usually develops around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy and affects about 3-8% of pregnancies globally. Although it typically resolves after childbirth, it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both mother and child.
How to Spot Gestational Diabetes
Some women may experience gestational diabetes symptoms, while others may have no symptoms at all. Common signs to look out for include:
- Increased thirst and dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue and feeling sluggish
- Blurred vision
- Increased hunger, even after eating
However, many women with gestational diabetes have no noticeable symptoms, which is why routine screening is so important.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Certain women may be at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes:
- Age: Women over the age of 25 are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese before pregnancy increases the risk.
- Family history: Having a close family member with diabetes increases the risk.
- Previous gestational diabetes: Women who had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are at higher risk.
How to Manage Gestational Diabetes Early
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes can prevent complications. Here are steps to manage the condition:
1. Screening and Diagnosis
Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed through a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. If you have risk factors, your doctor may recommend earlier testing. If diagnosed, your healthcare provider will develop a management plan tailored to your needs.
2. Healthy Diet
A balanced, diabetes-friendly diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Focus on:
- Whole grains instead of refined carbohydrates
- Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and legumes
- Non-starchy vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and cauliflower
- Limited sugary foods and processed snacks
Work with a nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that helps keep your blood sugar levels stable.
3. Regular Exercise
Moderate exercise, such as walking or pregnancy-safe yoga, can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week, but always consult your doctor before starting any exercise program during pregnancy.
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of pregnancy sugar levels is critical in managing gestational diabetes. Your doctor may advise you to check your blood sugar several times a day to ensure that your levels remain within the target range. Keeping a log of your readings will help your healthcare team make necessary adjustments to your diet or medication.
5. Medication
In some cases, insulin or oral medications may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. Insulin does not cross the placenta, making it a safe option for controlling blood sugar during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes are essential for the health of both the mother and the baby. Regular screenings, a healthy diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring are key components of managing the condition. If you’re pregnant and at risk of gestational diabetes, schedule regular checkups with your healthcare provider, and remember that MV Diabetes Hospital is here to support you with comprehensive care and management for a healthy pregnancy.
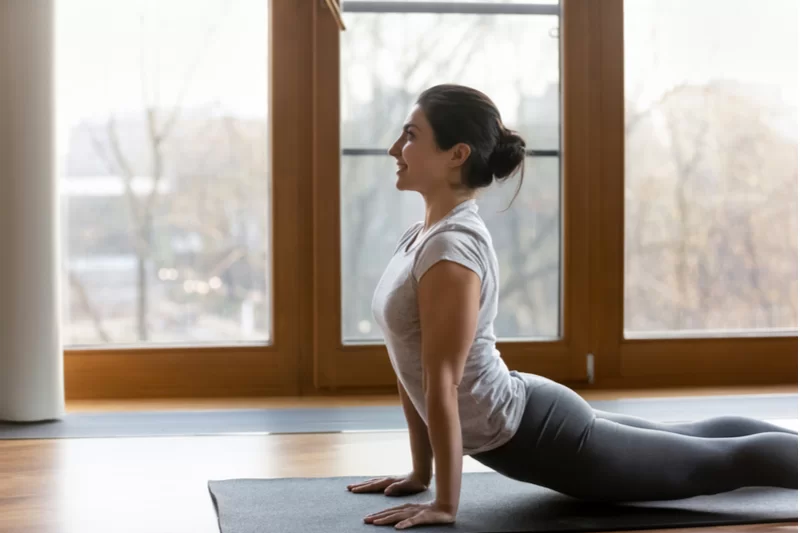

Top 5 Exercises for Diabetics to Control Sugar Levels
Introduction
Exercise is an essential component of managing diabetes, as it helps control blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and enhances overall health. Regular physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues. At MV Diabetes Hospital, we recommend various exercises that help control sugar levels and improve overall wellness for diabetic patients. In this blog, we’ll explore the top 5 exercises that are particularly beneficial for diabetics and can aid in sugar control workouts.
1. Brisk Walking
One of the easiest and most accessible exercises for diabetics is brisk walking. Walking can help lower blood sugar levels, improve circulation, and maintain a healthy weight. It’s also a low-impact exercise, making it suitable for most individuals, including those with joint problems.
Benefits:
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Walking regularly helps the body use insulin more effectively.
- Low impact: Walking is easy on the joints, making it suitable for people with different fitness levels.
- Cardiovascular health: It strengthens the heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease, a common issue for diabetics.
Tip: Aim for at least 30 minutes of brisk walking most days of the week. You can break it down into shorter sessions if needed.
2. Strength Training
Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, help build muscle mass, which in turn improves the body’s ability to store and use glucose. As we age, we naturally lose muscle mass, and strength training can help combat this loss while also improving metabolism.
Benefits:
- Boosts metabolism: Increasing muscle mass helps the body burn more calories and improves glucose utilization.
- Regulates blood sugar levels: Strength training improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for blood sugar control.
- Helps maintain healthy weight: Building muscle mass helps reduce body fat, which is essential for diabetes management.
Tip: Start with light weights or resistance bands, aiming for 2-3 strength training sessions per week.
3. Cycling
Cycling is a great cardiovascular exercise that provides an excellent workout for diabetics. It helps improve circulation, reduces stress, and controls blood sugar levels. Whether you prefer outdoor cycling or using a stationary bike, it’s an effective and enjoyable way to stay active.
Benefits:
- Enhances cardiovascular health: Regular cycling strengthens the heart and improves circulation.
- Burns calories: It helps in weight management, which is vital for diabetes control.
- Low-impact: Cycling is gentle on the joints, making it ideal for those with joint pain or mobility issues.
Tip: Aim for 20-30 minutes of cycling a few times a week. Adjust the intensity based on your fitness level.
4. Swimming
Swimming is a full-body workout that is easy on the joints and can help reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. It’s a great exercise for those with neuropathy or joint pain since the buoyancy of the water reduces stress on the body.
Benefits:
- Total body workout: Swimming engages all muscle groups, helping improve strength and flexibility.
- Regulates blood sugar: Swimming can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Improves heart health: Regular swimming strengthens the heart and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Tip: Start with 20-minute sessions and gradually increase the duration as your fitness level improves.
5. Yoga
Yoga is a holistic exercise that combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to promote overall well-being. It’s particularly beneficial for diabetics, as it reduces stress, improves blood circulation, and enhances flexibility. Specific poses can help control blood sugar levels and improve balance.
Benefits:
- Reduces stress: Yoga helps lower cortisol levels, which can negatively impact blood sugar control.
- Improves circulation: Many yoga poses promote better circulation, which is important for diabetes management.
- Enhances flexibility: Regular practice improves flexibility, which can help reduce stiffness and pain often associated with diabetes.
Tip: Try yoga classes specifically designed for diabetes management or use online resources. Aim for at least 20-30 minutes of yoga a few times a week.
Conclusion
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine is one of the most effective ways to control sugar levels and improve overall health. Whether it’s brisk walking, strength training, cycling, swimming, or yoga, finding an exercise you enjoy and can commit to is key. At MV Diabetes Hospital, we encourage our patients to engage in these activities to help manage their diabetes and improve their quality of life. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs.
Beyond Sugar Levels: A Holistic Approach to Living Well with Diabetes
For many people, managing diabetes becomes a numbers game – fasting sugar, post-meal sugar, HbA1c. But real health is more than a lab report.
A holistic approach to diabetes looks at your diet, lifestyle, mental health, treatment, and long-term goals together. This is where a specialised centre like MV Diabetes makes a powerful difference.
1. Mindset Shift: From “I Am Sick” to “I Am in Control”
The first step in holistic diabetes care is changing how you see the condition.
Diabetes is:
- Chronic (long-term) but manageable
- Strongly influenced by your daily choices
- Not your fault – but your responsibility
When patients move from fear to understanding, they make better decisions about food, exercise, medicine, and check-ups.
2. Food as Fuel, Not Enemy
A holistic plan always begins with a realistic diabetes diet:
- Respect your culture and taste
- Adjust portions, timing, and combinations
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
- Preserve enjoyment of meals while protecting health
This approach avoids extreme diets and encourages sustainable eating habits that work for families, not just individuals.
3. Movement as Medicine
Instead of thinking “I must exercise”, holistic care reframes it as:
- “I am giving my body energy and flexibility”
- “I am protecting my heart, joints, and mind”
Combining:
- Daily walking or aerobic activity
- Simple strength training
- Regular breaks from long sitting (especially for office jobs)
This supports blood sugar control, weight management, and mood.
4. Emotional and Mental Health
Living with diabetes can be emotionally exhausting:
- Constant monitoring
- Fear of complications
- Guilt over food choices
- Pressure from family or work
Holistic care includes:
- Counselling and support groups
- Stress management strategies
- Encouraging family involvement in a positive way
Keywords: “diabetes and mental health”, “stress management in diabetes” are highly relevant and often searched.
5. Regular Monitoring and Early Detection
Holistic doesn’t mean “no tests”. In fact, it means the right tests at the right time:
- Blood sugar profile
- HbA1c
- Lipid profile
- Kidney function tests
- Eye screening
- Foot examination
- Blood pressure monitoring
At centres like MV Diabetes, all of this is integrated into a comprehensive diabetes check-up, making it convenient and thorough.
6. Working With a Team, Not Just a Prescription
A true holistic diabetes programme usually involves:
- Diabetologist / endocrinologist – leads your treatment
- Dietitian – designs diabetes diet plans
- Diabetes educator – teaches monitoring and self-care
- Foot specialist, eye specialist, heart specialist – screens and treats complications when needed
- Counsellor / psychologist – supports emotional well-being
This multidisciplinary care ensures that no part of your health is ignored.
7. Personal Goals: What Does “Healthy” Mean for You?
Holistic diabetes management is not only about avoiding complications. It’s also about your life goals:
- Do you want to play with your grandchildren without getting tired?
- Travel more confidently?
- Lose weight and feel lighter?
- Avoid hospital admissions?
Your treatment, diet, lifestyle, and follow-up plan should be aligned with these real-life goals – and updated regularly as life changes.

The Latest Advancements in Diabetes Treatment: What Patients Should Know
Diabetes care has changed dramatically over the last few decades. From basic tablets and injections, we have moved into an era of smart devices, newer medications, and personalised treatment plans.
If you or your family member is living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, understanding these new diabetes treatments can help you ask better questions and get better care.
1. Newer Diabetes Medications: Beyond Just Sugar Control
Today, many modern diabetes medicines not only lower blood sugar but also protect your:
- Heart
- Kidneys
- Weight
- Overall long-term health
Some commonly used newer classes (your doctor will decide what suits you):
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- SGLT2 inhibitors – some also protect kidneys and heart
- GLP-1 receptor agonists – can help with weight loss and heart protection
- Newer insulin analogues – smoother action, fewer lows
These keywords – “latest diabetes tablets”, “new insulin types”, “best treatment for type 2 diabetes” – also perform well in search.
2. Insulin Advancements: Safer and Smarter
Modern basal-bolus insulin regimens, insulin pens, and insulin analogues have:
- More predictable action
- Lower risk of hypoglycemia (low sugar)
- Greater flexibility with meals and lifestyle
For some patients, insulin pumps and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) can offer even more precise control, especially in type 1 diabetes.
3. Technology in Diabetes: From Finger Pricks to Sensors
The rise of diabetes technology has transformed daily management:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Small sensors measure sugar levels every few minutes and show trends.
- Flash Glucose Monitoring: Scan a sensor to see your current glucose and patterns.
- Smartphone apps that sync data and generate easy-to-understand reports.
These tools help your diabetologist see when your sugar goes high or low and adjust insulin and diet more precisely.
4. Precision and Personalised Diabetes Care
Not every patient is the same. The best diabetes treatment plan considers:
- Age
- Type of diabetes
- Weight and lifestyle
- Other health conditions (heart disease, kidney issues, etc.)
- Risk of hypoglycemia
- Patient preferences
At MV Diabetes, doctors use detailed investigations, regular follow-ups, and modern tools to provide personalised diabetes care for each individual, not just “one-size-fits-all” prescriptions.
5. Focus on Preventing Complications, Not Just Treating Them
Modern diabetes care is shifting from reactive (treating complications after they occur) to proactive (preventing them as much as possible).
This includes:
- Early screening for diabetic retinopathy (eye damage)
- Regular urine and blood tests for diabetic kidney disease
- Foot examinations for diabetic neuropathy and ulcers
- Heart risk assessment and cholesterol control
Search terms like “how to prevent diabetes complications”, “diabetic eye check-up”, “foot care for diabetes” are commonly used by patients.
6. Education as Treatment
One of the biggest advancements in diabetes management isn’t a machine or a tablet – it’s structured diabetes education.
When patients learn:
- How food affects sugar
- How to adjust activity levels
- When to check sugar
- How to recognise and treat lows
…their outcomes improve dramatically.
That’s why centres like MV Diabetes invest heavily in diabetes educators, dietitians, and counsellors.